SUNDSTRAND (VARIABLE DISPLACEMENT HYDROSTATIC PUMP) AND (FIXED DISPLACEMENT
HYDROSTATIC MOTOR), PAGES 49 THRU 61.
HYDRAULIC CIRCUITS
the pump to the displacement of the motor will
determine the speed of the motor output shaft. Moving
GENERAL
the control lever to the opposite side of neutral, the flow
The hydrostatic transmission offers an infinite control of
from the pump is reversed and the motor output shaft
speed and direction. The operator has complete control
turns in the opposite direction. Speed of the output
of the system with one lever for speed and direction.
shaft is controlled by adjusting the displacement (flow)
of the pump.
Control of the variable displacement, axial piston pump
The pump and motor are contained in separate
is the key to controlling the roller. Engine horsepower is
housings. All valves required for a closed loop circuit
transmitted to the pump. When the operator moves the
are included in either the pump or motor assemblies. A
control lever, the swashplate in the pump is tilted from
reservoir, filter, cooler and lines complete the circuit.
neutral.
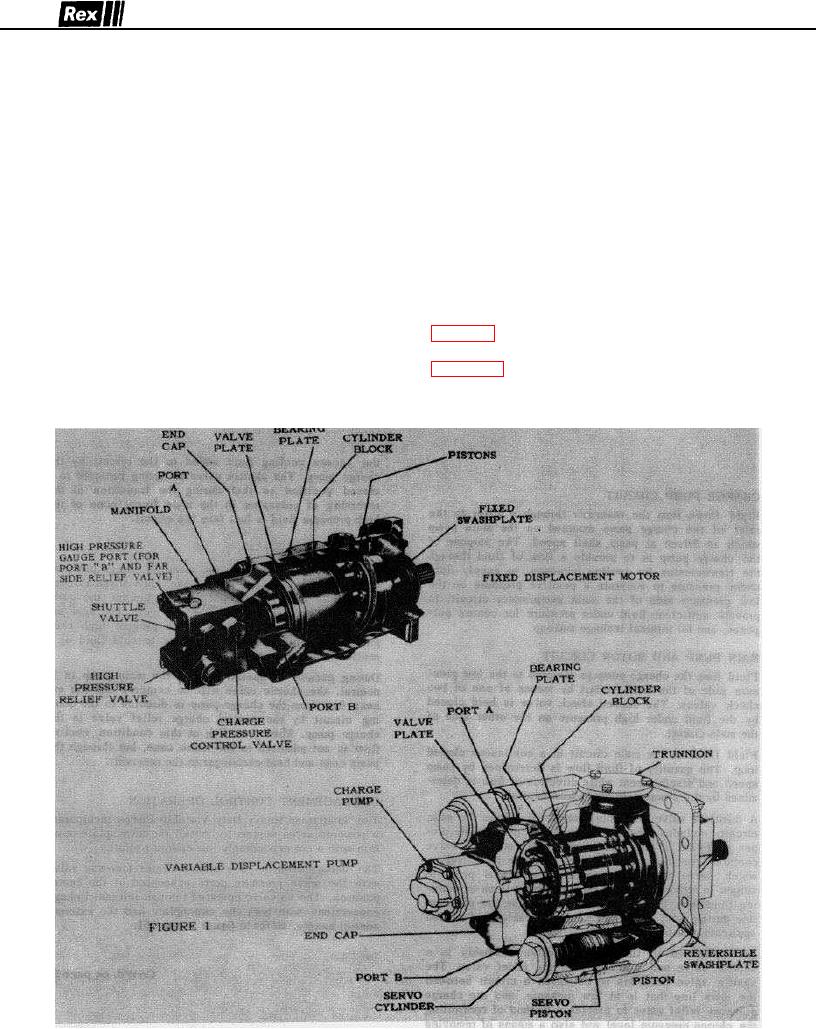
Figure 1 illustrates the internal components of a typical
When the variable pump swashplate is tilted, a positive
Sundstrand heavy duty hydrostatic transmission.
stroke to the pistons is created. This, in turn, at any
Figure 2 illustrates the general appearance of the
given input speed, produces a certain flow of oil from
components of a heavy duty transmission.
the pump. This flow is transferred through high pressure
lines to the motor. The ratio of the volume of flow from
FIGURE 1

