1.6
DETROIT DIESEL 53
P I S T O N AND PISTON RINGS
hardened, floating piston pin. After the piston pin has
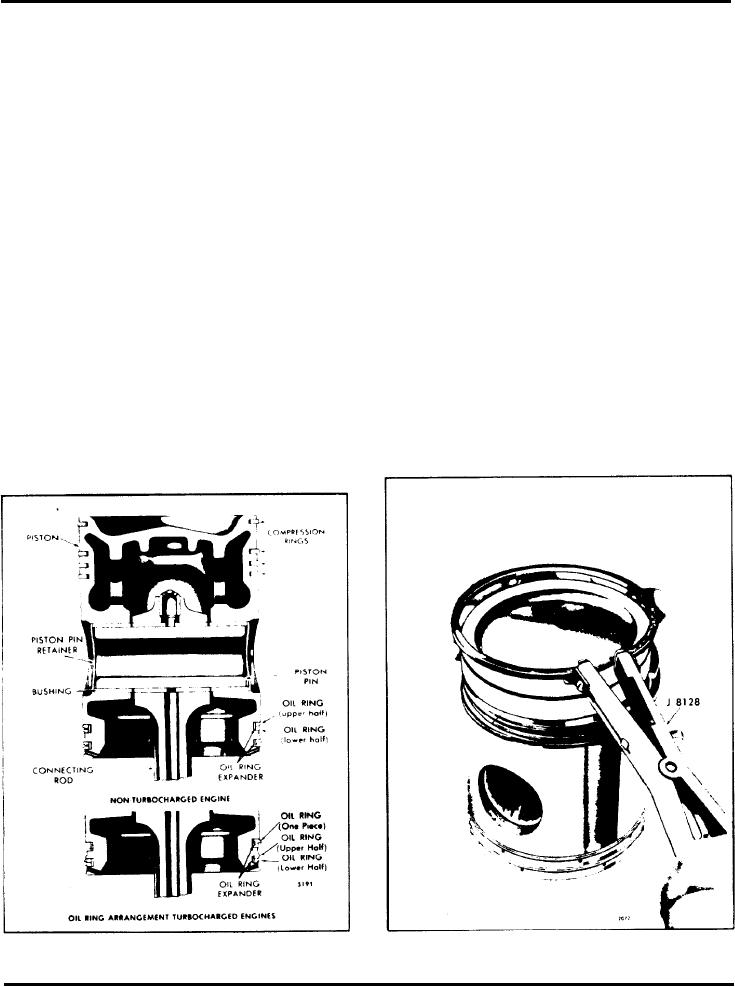
The trunk type malleable iron piston (Fig. 1) is plated
been installed, the hole in the piston at each end of the
with a protective coating of the which permits close
pin is sealed with a steel retainer. Thus lubricating oil
fitting. reduces scuffing and prolongs piston life. The
returning from the sprayed underside of the piston
top of the piston forms the combustion chamber bowl
head and working through the grooves in the piston
and is designed to compress the air into close
pin bushings is prevented from reaching the cylinder
proximity to the fuel spray.
walls.
Each piston is internally braced with fin-shaped ribs
and circular struts. scientifically designed to draw heat
Each piston is fitted with compression rings and oil
rapidly from the piston crown and transfer it to the
control rings (Fig. 1 ).
lubricating oil spray to ensure better control of piston
ring temperature.
Equally spaced holes arc drilled just below each oil
control ring land to permit the excess oil that is
The piston is cooled by a spray of lubricating oil
scraped off the cylinder walls to return to the
directed at the underside of the piston head from a
nozzle in the top of the connecting rod, by fresh air
from the blower to the top of the piston and indirectly
by the water Jacket around the cylinder.
Inspect Piston Rings
Each piston is balanced to close limits by machining a
balancing rib. provided on the inside at the bottom of
When an engine is hard to start, runs rough or lacks
the piston skirt.
power, worn or sticking compression rings may he the
cause. Replacing the rings will aid in restoring engine
Two bushings, with helical grooved oil passages, are
operation to normal.
pressed into the piston to provide a bearing for the
Fig. 2 - Removing or Installing Piston Ring
Fig. 1 - Typical Piston Assembly
SEC. 1.6 Page 1
April, 1974

