Fuel Oil and Coolant Specifications
DETROIT DIESEL
GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS
The quality of fuel oil used for high-speed diesel engine operation is a very important factor in obtaining satisfactory
engine performance, long engine life, and acceptable exhaust. Fuel selected should be completely distilled material.
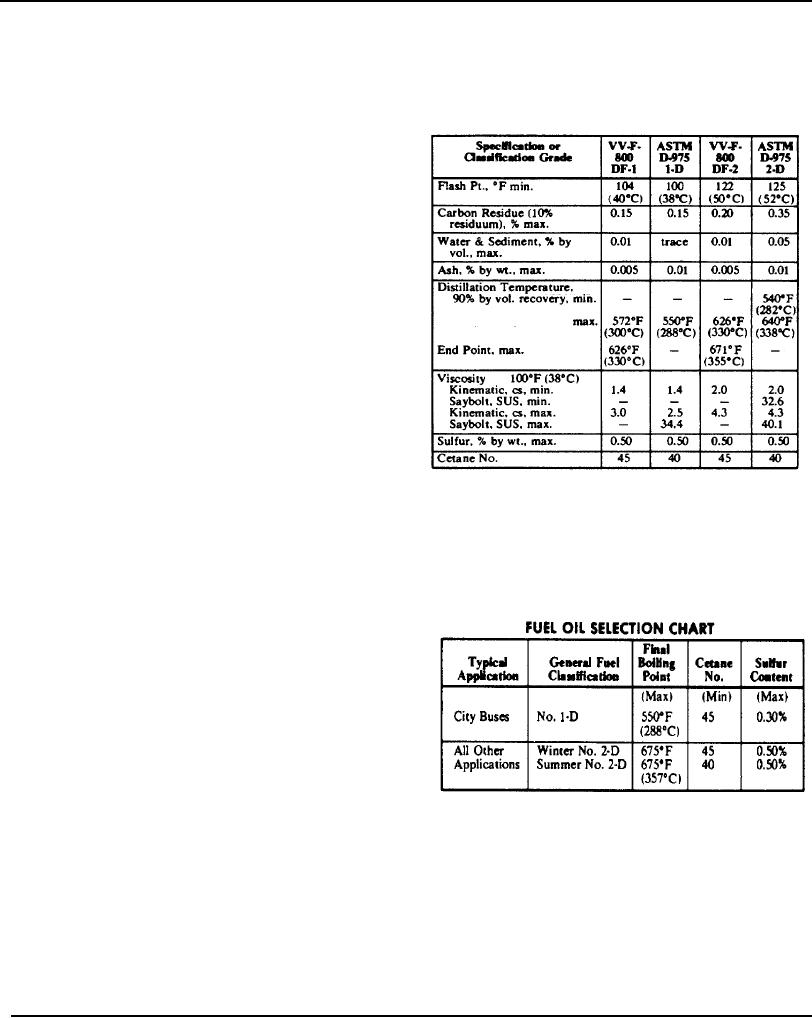
Fuels marketed to meet Federal Specification VV-F-800 (grades DF-I and DF-2) and ASTM Designation D-975 (grades I-
D and 2-D) meet the completely distilled criteria. Some of the general properties of VV-F-800 and ASTM D-975 fuels are
shown below.
FEDERAL SPECIFICATION A ASTMDIESEL FUEL PROPERTIES
Residual fuels and domestic furnace oils are not considered
satisfactory for Detroit Diesel engines; however, some may
be acceptable.
(See "DETROIT DIESEL FUEL OIL
SPECIFICATIONS").
NOTE: Detroit Diesel Allison does
not
recommend the use of drained lubricating oh as a
diesel fuel oil.
All diesel fuel oil contains a certain amount of sulfur. Too
high a sulfur content results in excessive cylinder wear due
to acid build-up in the lubricating oil. For most satisfactory
engine life, fuels containing less than 0.5% sulfur should be
used. Fuel oil should be clean and free of contamination.
Storage tanks should be inspected regularly for dirt, water or
water-emulsion sludge, and cleaned if contaminated.
Storage instability of the fuel can lead to the formation of
varnish or sludge in the tank. The presence of these
contaminants from storage instability must be resolved with
the fuel supplier.
SPECIFICATIONS
Detroit Diesel Allison designs, develops, and manufactures commercial diesel engines to operate on diesel fuels
classified by the ASTM as Designation D-975 (grades I-D and 2-D). These grades are very similar to grades DF-1 and
DF-2 of Federal Specification VV-F-800. Residual fuels and furnace oils, generally, are not considered satisfactory for
Detroit Diesel engines. In some regions, however, fuel suppliers may distribute one fuel that is marketed as either diesel
fuel (ASTM D-975) or domestic heating fuel (ASTMD-396) sometimes identified as furnace oil. In this case, the fuel
should be investigated to determine whether the properties conform with those shown in the "FUEL OIL SELECTION
HART" presented in this specification.
The "FUEL OIL SELECTION CHART" also will serve as a
guide in the selection of the proper fuel for various
applications. The fuels used must be clean, completely
distilled, stable, and non-corrosive. DISTILLATION RANGE,
CETANE NUMBER, and SULFUR CONTENT are three of
the most important properties of diesel fuels that must be
controlled to insure optimum combustion and minimum
wear.
Engine speed, load, and ambient temperature
influence the selection of fuels with respect to distillation
range and cetane number. The sulfur content of the fuel
must be as low
as possible to avoid excessive deposit formation, premature
wear, and to minimize the sulfur dioxide exhausted into the
atmosphere.
To assure that the fuel you use meets the required properties, enlist the aid of a reputable fuel oil supplier. The
responsibility for clean fuel lies with the fuel supplier as well as the operator. During cold weather engine operation, the
cloud point (the temperature at which wax crystals begin to form in diesel fuel) should be 10F (6C) below the lowest
expected fuel temperature to prevent clogging of the fuel filters by wax crystals. At temperatures below -20F (-29C),
consult an authorized Detroit Diesel Allison service outlet, since particular attention must be given to the cooling system,
lubricating system, fuel system, electrical system, and cold weather starting aids for efficient engine starting and
operation.
NOTE: When prolonged idling periods or cold weather conditions below 32F (0C) are encountered, the use of lighter
distillate fuels may be more practical. The same consideration must be made when operating at altitudes above 5,000 ft.
Page 66

