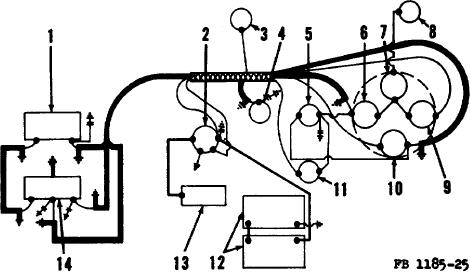
switch (2), starter button (11),starting motor (13), and wiring. The starting circuit is designed to carry high current with a
minimum loss of voltage. When the starter button (11) is depressed, the electrical current from the battery (12) operates
the magnetic switch (2) and flows to the starting motor (13). The starting motor converts the electric current into a
mechanical force used to crank the engine.
Caution: When electrical components are removed or installed, the battery ground cable should
be disconnected from the battery terminal to prevent accidental arcing at the electrical
connections.
1
Battery generator
8
Fuel gage transmitter
2
Magnetic switch
9
Oil pressure gage
3
Oil pressure sender
10
4
Temperature sender
11
Starter button
5
Ignition switch
12
Battery
6
Temperature gage
13
Starting motor
7
Fuel gage
14
Voltage regulator
Figure 25. Practical wiring diagram.
b. The Charging Circuit. The charging circuit includes the generator (1), voltage regulator (14), battery (12), ammeter
(10), and wiring. The generator (1) produces the electric current, and the voltage regulator (14) controls the output of the
generator to conform to the requirements of the circuits.
c. The Ignition Circuit. The ignition circuit includes the magneto, shielded spark plug leads, and spark plugs. The
magneto produces electric current and directs it at properly timed intervals to the spark plugs.
111. Battery and Cables
a. General. The battery converts the electricity into chemical energy which is stored until the battery is connected to
an external
86

